EDB Notes Reduction of Oil and Gas Share in Mutual Trade between the Bank's Member States
Moscow, December 12, 2017. – Preliminary results for 2017 indicate that, in quality terms, macroeconomic metrics posted by EDB member states look relatively favorable. However, external risks remain quite significant, which underscores the relevance of qualitative shifts that have been unfolding within EDB economies against the background of reassuring quantitative indicators.
This conclusion is presented in the monthly macroeconomic review prepared by the EDB Chief Economist Group.
"The most notable qualitative shifts in the operation of EDB economies, primarily as regards ongoing reduction of their dependence on raw materials, include reduction of dependence of national currency exchange rates and regional financial markets on raw material price fluctuations, reduction of the share of oil and gas revenues in non-oil/gas deficit in the federal budget of the Russian Federation, and reduction of raw material (oil and gas) bias in mutual trade between EAEU member states," said Yaroslav Lisovolik, EDB Chief Economist.
In the fiscal area, EDB analysts note a considerable decrease in the share of oil and gas revenues in the federal budget of the Russian Federation: while prior to 2014 they accounted for more than 50%, in January-September 2015 that indicator went down to 44.5%, reaching 38.7% over the first 9 months of 2017[1]. Other positive trends cited by the authors of the review include reduction of oil and gas budget deficit of the Russian Federation (an indicator of fiscal sensitivity to falling oil prices) – that indicator decreased from 8.5% of the GDP in January-September 2015 to 6.8% of the GDP in January-September 2017.
EDB analysts have paid special attention to the 2017 decline of the raw material bias in EAEU exports, particularly as regards Russian oil and gas exports. The role of raw materials has also sustained a slight reduction in mutual trade between EAEU member states.
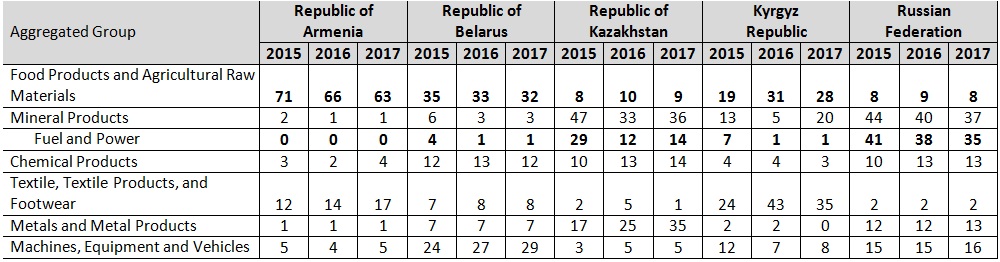
Thus, in January-September 2017, the share of Mineral Products in mutual trade between the Russian Federation and its EAEU partners decreased to 37% from 40% the year before, while in Kazakhstan that indicator posted a modest increase. On the whole, the share of Minerals and Food Products in mutual trade between EAEU member states has gone down by more than 1 p.p., while the shares of Machines and Equipment and Metals and Metal Products are up by 1 p.p. and almost by 2 p.p., respectively. In terms of changes in mutual trade between EAEU member states, the only segments in which all union members have posted growth in January-September 2017 are Food Products and Machines and Equipment. In the opinion of EDB analysts, these changes in the share of raw materials in mutual trade between EAEU member states have even more pronounced positive overtones if we take into consideration the growth of oil prices in 2017.
In the Republic of Armenia, the shares of Textiles and Machines and Equipment in January-September 2017 have increased by 3 p.p. and 1 p.p. year-on-year, respectively. Over the last two years, the share of Machines and Equipment in mutual trade between the Republic of Belarus and other EAEU member states has increased by 5 p.p. In Kazakhstan, the increase of the share of Mineral Products in January-September 2017 by 3 p.p. year-on-year was accompanied by a sizeable growth of the share of Metals and Metal Products from 25% to 35% over the same period of time.
The authors of the review believe that such trends, despite certain progress in reducing dependence on fuel and power prices, are still not well established, while the rates of their expansion within the EAEU are quite uneven. Accordingly, it is critical to pursue in 2018 a macroeconomic policy that will encourage further reduction of dependence of regional economies on raw materials, among other things, by reinforcing the significance of economic rules.
The full version of the monthly macroeconomic review is available here.
All monthly macroeconomic reviews are published here.
Changes in the Structure of Mutual Trade between EAEU Member States over 9 Months, % of Total Exports
Source: EEC, in-house calculations
[1] Here and below mutual trade data for January-September are the latest official data for 2017 made available by the EEC.
Additional Information:
Eurasian Development Bank (EDB) is an international financial institution founded by Russia and Kazakhstan in January 2006 to promote development of market economies of its member states, and secure their sustainable economic growth and expansion of their mutual trade and economic ties. The charter capital of the EDB is $ 7 billion. The member states of the Bank are the Republic of Armenia, the Republic of Belarus, the Republic of Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, the Russian Federation, and the Republic of Tajikistan.
More detailed information on the EDB is available at https://eabr.org/.
EDB Media Center:
+7 (727) 244 40 44 ext. 6147 (Almaty)
+7 (495) 645 04 45 ext. 2732 (Moscow)
e-mail: pressa@eabr.org
